
It may take some time for the muscles to regain their strength if the limb has been held still in a backslab. There is no ongoing weakness of the bone following a buckle fracture. Will the fracture area be weaker forever? This is because the bone does not move out of alignment (correct position) and the fracture is small. In nearly all cases, buckle fractures heal quickly and with no complications. Why doesn’t my child need a follow-up appointment? Kids Health Info fact sheet: Plaster cast care.Avoid contact sports for six weeks after the injury.Most children will not need a follow-up appointment or X-ray, because buckle fractures usually heal quickly without any problems.Your child should wear a removable backslab (partial cast) or splint for three weeks.A buckle fracture in the wrist is a small area of compressed bone.your child will not use their wrist, hand or fingers within two to three days of the back slab or splint being removed.your child’s wrist remains very painful or swollen three weeks after the injury.Contact sports (or rough and tumble play) should be avoided for six weeks after the injury. Wrist movement may be a little stiff and sore at first. Three weeks after their injury, your child can just stop wearing their backslab or splint. Further X-rays or physiotherapy are usually not required. Never cut or attempt to modify the cast, and make sure you avoid getting it wet.īecause buckle injuries are stable and heal quickly without problems, most children will not need a follow-up appointment with the GP or hospital. Give the pain relief medication as required, following the directions on the packet or as directed by the

Although immobilising the arm with the backslab or splint will help to reduce the pain, additional pain relief (e.g. An arm sling is optional, and may help reduce any pain orīuckle injuries may be painful. If you think your child has a fracture and you are looking for first aid advice, see our fact sheetīuckle injuries are treated by wearing a removable backslab (a partial cast held in place with bandages) or ready-made splint, which should be worn as much as possible but can be removed for bathing or showering. This fact sheet provides information on what to do once your child has been treated in hospital for a buckle injury. There is no deformity in the wrist, which means the wrist will The wrist may be tender, slightly swollen, and painful to move. The bone will have a very small fracture, which is so minor that it may be difficult to see on X-ray. Statistical data in this article was reviewed by the AAOS Department of Research and Scientific Affairs.A buckle injury of the wrist is a small area of compressed bone. Your doctor may recommend follow-up visits for up to one year to ensure that growth is proceeding normally.
If the fracture disrupts the growth plate at the end of the bone, it could affect the development of the bone. To allow the bones to safely regain their normal strength, the child should avoid playing on playground structures, such as monkey bars, for 3 to 4 weeks after the cast is removed. This stiffness will go away on its own, usually without the need for physical therapy.įor a short period of time, the forearm bones may be weaker due to immobilization in the cast. When the cast is removed, the wrist and elbow joints may be stiff for 2 to 3 weeks. A more serious injury, such as a Monteggia fracture, may need to be immobilized for 6 to 10 weeks. A stable fracture, such as a buckle fracture, may require 3 to 4 weeks in a cast. The length of time the cast is worn will vary depending on the severity of the fracture. Because the growth plate helps determine the future length and shape of the mature bone, this type of fracture requires prompt attention. In most cases, this type of fracture occurs in the growth plate of the radius near the wrist. Also called a "physeal" fracture, this fracture occurs at or across the growth plate. This is a very severe injury and requires urgent care. There is usually a fracture in the ulna and the top (head) of the radius is dislocated. This injury affects both bones of the forearm. There is usually a displaced fracture in the radius and a dislocation of the ulna at the wrist, where the radius and ulna come together. The fracture extends through a portion of the bone, causing it to bend on the other side. The fracture is across the upper or lower portion of the shaft of the bone and does not affect the growth plate.
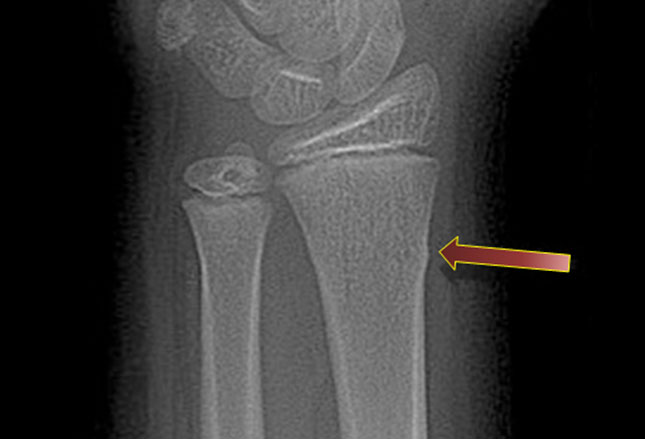
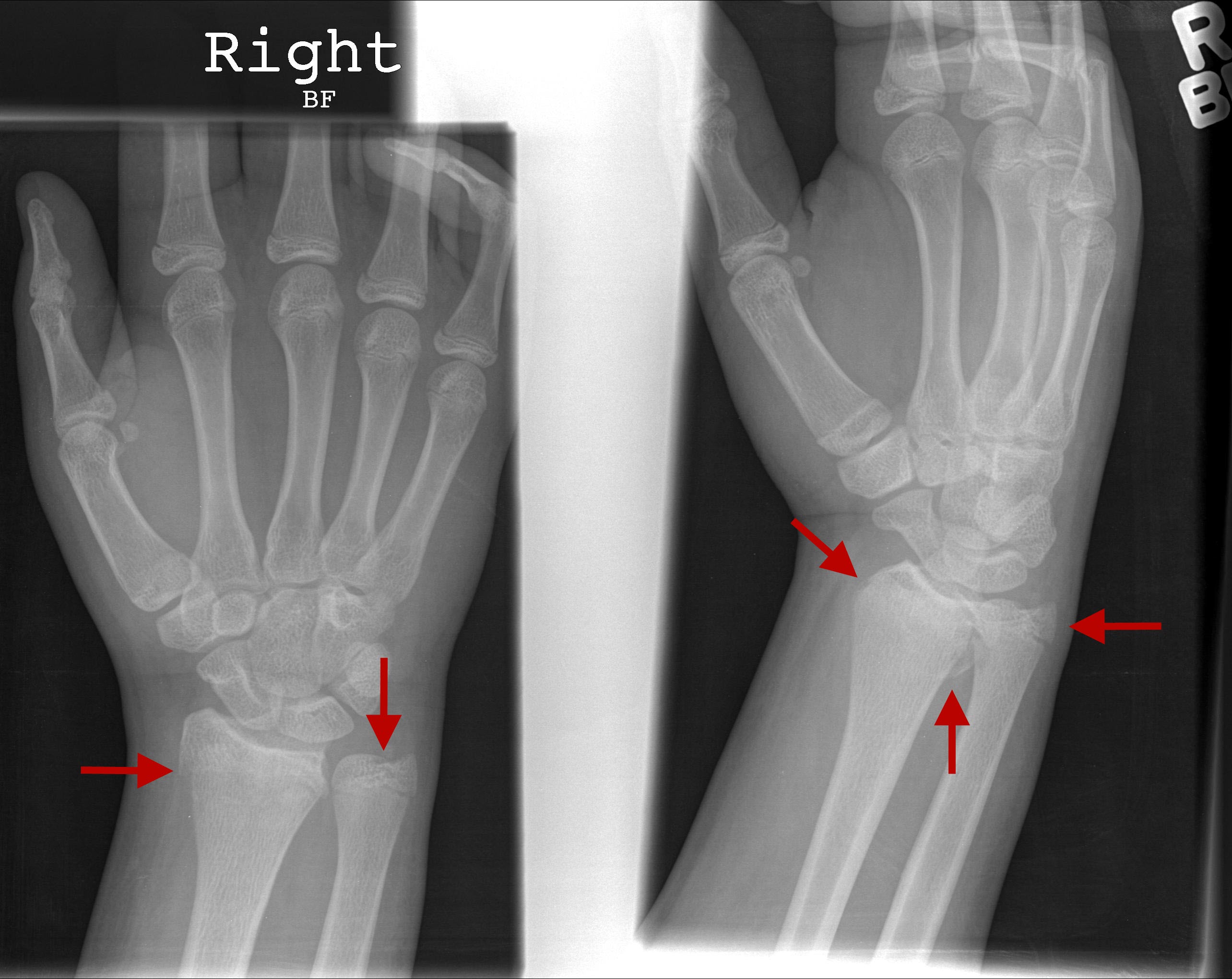
This is a stable fracture, meaning that the broken pieces of bone are still in position and have not separated apart (displaced). The topmost layer of bone on one side of the bone is compressed, causing the other side to bend away from the growth plate. There are several types of forearm fractures in children:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
